保护数据完整性与机密性:探索PGP的四种典型应用场景
- 作者
🔐 PGP(Pretty Good Privacy)在数字通信中的使用主要涵盖四种场景:加签(Signing)、验签(Verifying)、加密并加签(Encrypting and Signing)、以及解密并验签(Decrypting and Verifying)。这些场景体现了PGP在确保通信安全性和身份验证方面的多样性和复杂性。
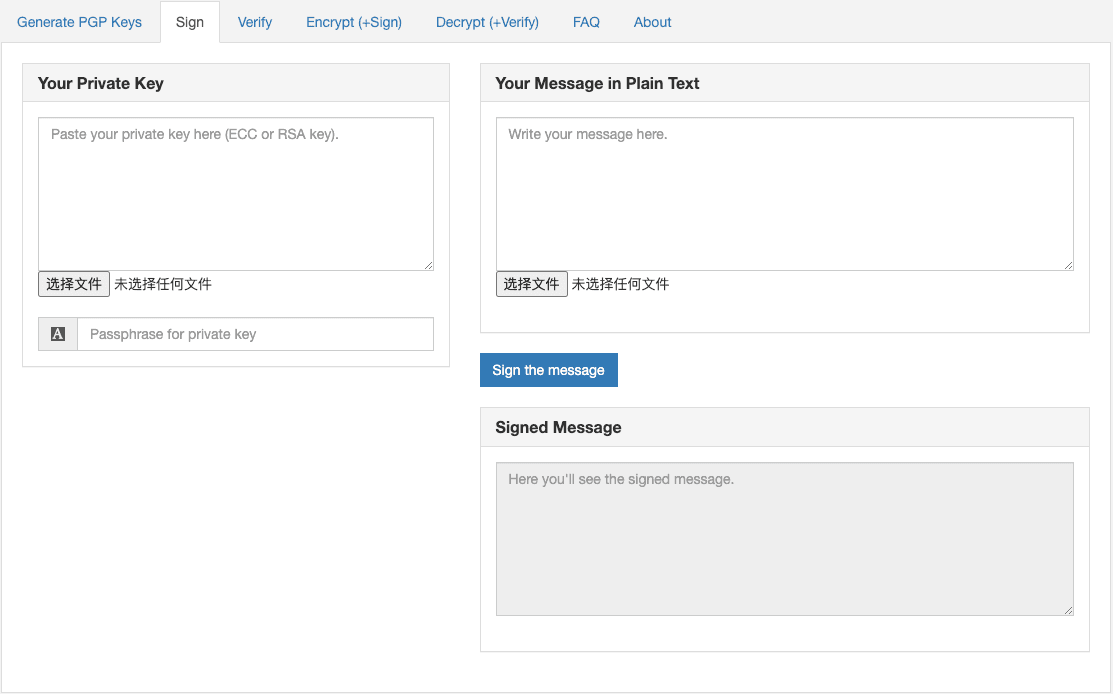
1. 加签(Signing)
- 场景描述:当发送者(如Alice)想要确认她的信息是真实的并且在传输过程中未被篡改时使用。
- 操作步骤:
- Alice使用自己的私钥对消息的散列(哈希)值进行加密,从而创建数字签名。
- 结果:该数字签名随消息一起发送,允许接收者验证消息的完整性和发送者的身份。
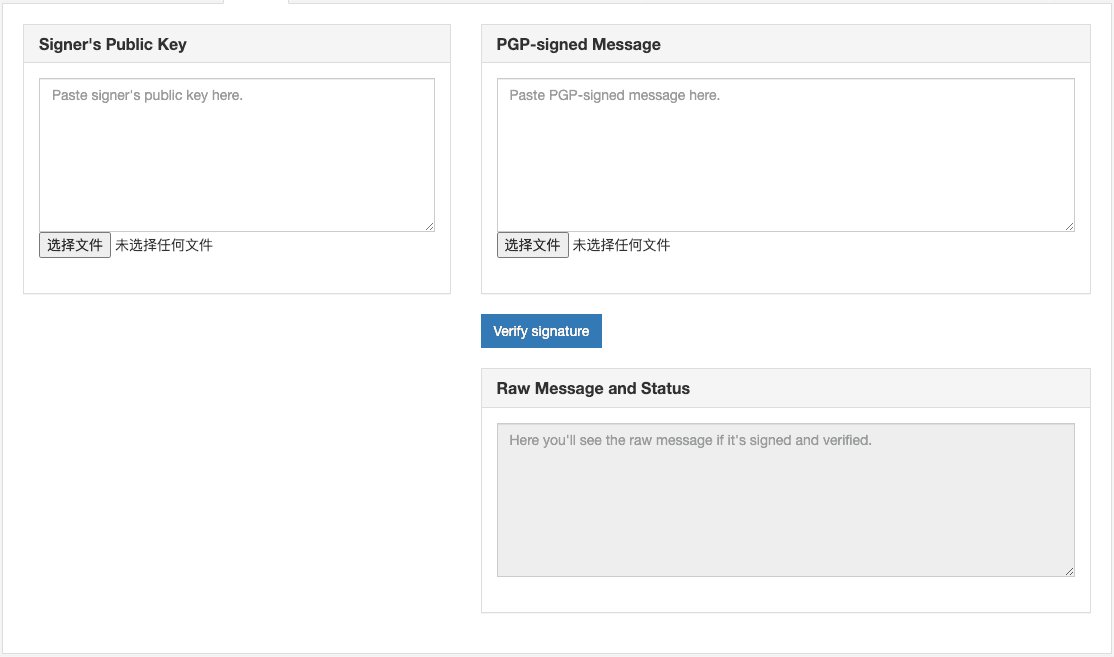
2. 验签(Verifying)
- 场景描述:当接收者(如Bob)收到一个带有数字签名的消息时,他需要验证这个消息确实来自声称的发送者,并且内容未被篡改。
- 操作步骤:
- Bob使用发送者(Alice)的公钥对数字签名进行解密,并将解密得到的散列值与消息当前的散列值进行对比。
- 结果:如果两个散列值匹配,证明消息未被篡改,且确实是Alice发送的。
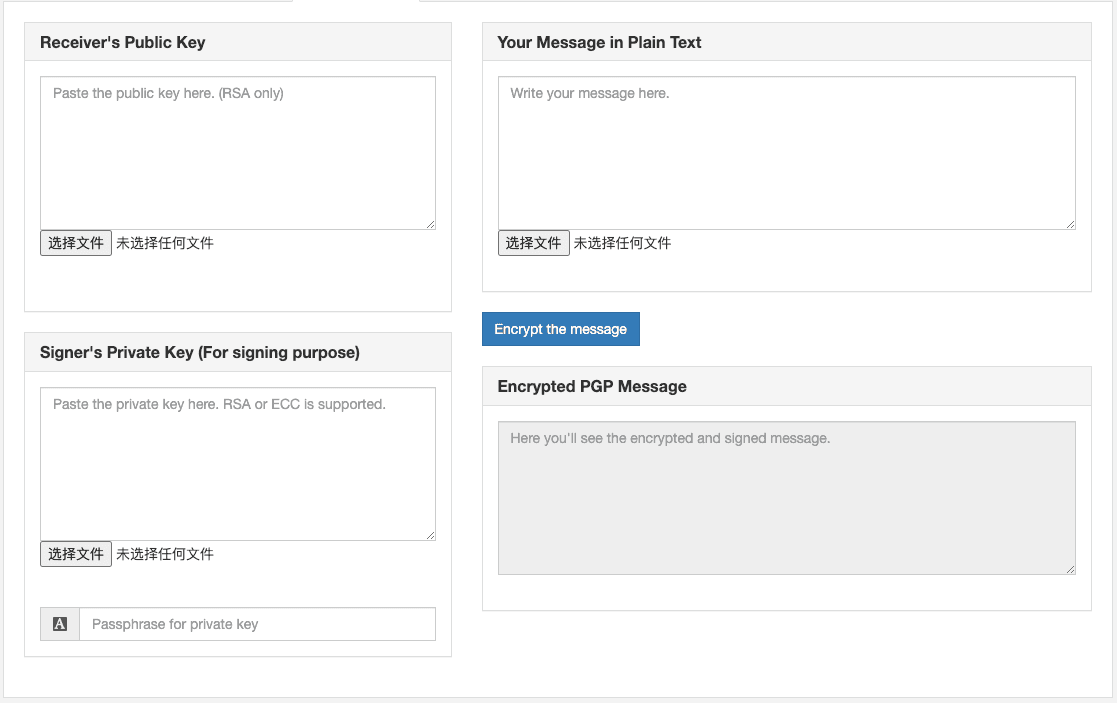
3. 加密并加签(Encrypting and Signing)
- 场景描述:在发送者需要确保消息的机密性和验证自己身份的情况下使用。
- 操作步骤:
- Alice首先对消息进行数字签名。
- 然后,她使用接收者(Bob的)公钥对已签名的消息进行加密。
- 结果:这确保了消息在传输过程中的安全性,并且接收者可以验证发送者的身份。
Java 代码示例:
public String encryptAndSign(String unencryptedMessage,
String senderUserIdEmail,
String senderPassphrase,
ArmoredKeyPair senderArmoredKeyPair,
String receiverUserId,
String receiverArmoredPublicKey)
throws IOException, PGPException, NoSuchAlgorithmException, SignatureException, NoSuchProviderException {
InMemoryKeyring keyring = keyring(senderPassphrase, senderArmoredKeyPair, receiverArmoredPublicKey);
ByteArrayOutputStream encryptedOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
try (
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(encryptedOutputStream);
OutputStream bouncyGPGOutputStream = BouncyGPG.encryptToStream()
.withConfig(keyring)
.withStrongAlgorithms()
.toRecipient(receiverUserId)
.andSignWith(senderUserIdEmail)
.armorAsciiOutput()
.andWriteTo(bufferedOutputStream)
) {
Streams.pipeAll(new ByteArrayInputStream(unencryptedMessage.getBytes()), bouncyGPGOutputStream);
}
return encryptedOutputStream.toString(UTF_8.name());
}
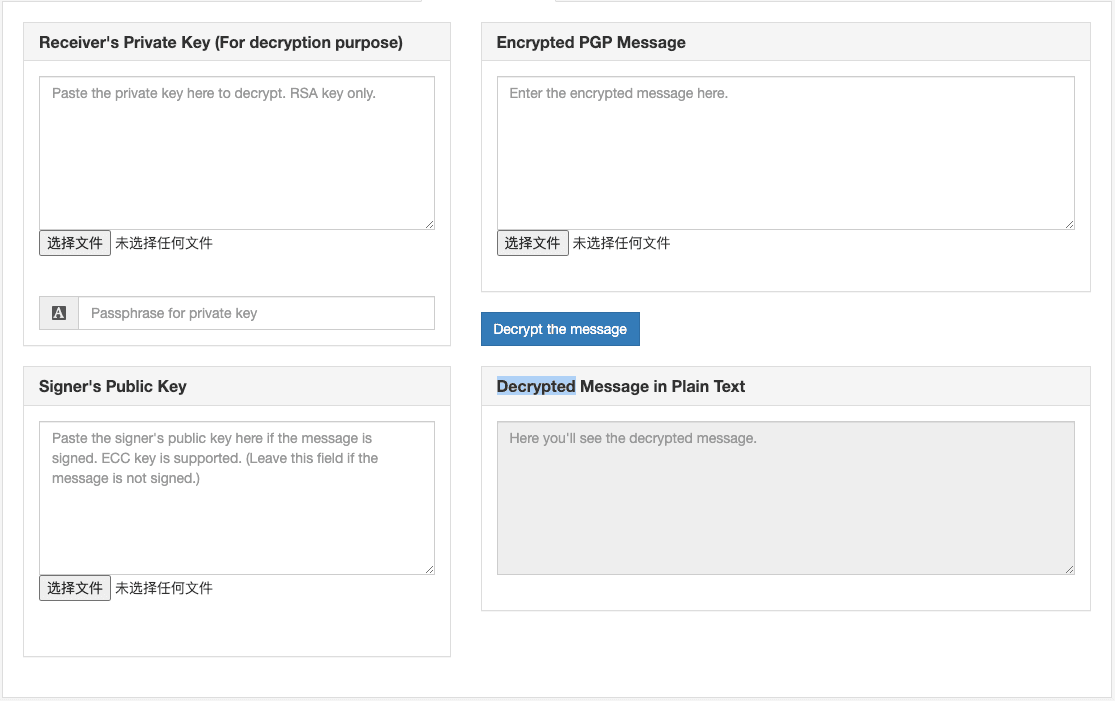
4. 解密并验签(Decrypting and Verifying)
- 场景描述:当接收者需要读取加密的消息内容并验证发送者身份时使用。
- 操作步骤:
- Bob首先使用自己的私钥对消息进行解密。
- 解密后,他使用发送者(Alice)的公钥来验证消息上的数字签名。
- 结果:Bob不仅能够阅读消息内容,还能确认消息的真实来源和完整性。
Java 代码示例:
public String decryptAndVerify(String encryptedMessage,
String receiverPassphrase,
ArmoredKeyPair receiverArmoredKeyPair,
String senderUserIdEmail,
String senderArmoredPublicKey)
throws IOException, PGPException, NoSuchProviderException {
InMemoryKeyring keyring = keyring(receiverPassphrase, receiverArmoredKeyPair, senderArmoredPublicKey);
ByteArrayOutputStream unencryptedOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
try (
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(unencryptedOutputStream);
InputStream bouncyGPGInputStream = BouncyGPG
.decryptAndVerifyStream()
.withConfig(keyring)
.andRequireSignatureFromAllKeys(senderUserIdEmail)
.fromEncryptedInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(encryptedMessage.getBytes(UTF_8)))
) {
Streams.pipeAll(bouncyGPGInputStream, bufferedOutputStream);
}
return unencryptedOutputStream.toString(UTF_8.name());
}
总结
这四种场景共同构成了PGP在数字通信中的核心应用,提供了一套全面的机制,用于保护信息的机密性、完整性和验证消息来源。PGP Tool - Online PGP Key Generator Encryption Decryption Tool 提供了线上生成 PGP Key、加签验签、加密解密的工具,如果需要更深的理解 PGP 的原理,可以线上使用该工具实际操作一下。Java 代码可以参考 PGP Example 里面的示例。
分享内容